Why Is It Harder to Read With Contacts
Lesson 2: Why is it And so Difficult to Make Decisions?
/en/problem-solving-and-determination-making/what-is-disquisitional-thinking/content/
The challenge of making decisions
No thing who you are or what you practise for a living, you make thousands of minor decisions every day. Almost are relatively inconsequential; for example, what practise you want for breakfast? Do you want coffee, tea, or something else?

Other decisions are much more complex. Should yous take a new job? Should you lot motion to a different city? What about buying a house, or starting a family? These decisions weigh more heavily considering they can impact your life in many ways.

You might feel like you're bad at making decisions (or non good at making skilful ones). However, it's something we all struggle with due to the way our brains are made. Behind every decision, there are underground psychological factors that shape the style nosotros think and act. Agreement these factors can make them easier to overcome.
Watch the video below to acquire more near the psychology of decision-making.
Condition quo bias
Many missteps in decision-making can exist chalked upwardly to cognitive bias. That'south our trend to think a certain way without even realizing it. Here'due south a elementary example: Have you ever avoided switching Internet providers, even though you were unhappy with your electric current service?
Something called status quo bias might exist to blame. That'south our trend to stick with what we know, instead of choosing something new and different. We see the alternative as a risk or just not worth the trouble, fifty-fifty if information technology might be better. Without realizing it, we tin become overly resistant to change.

Anchoring bias
Anchoring bias tin can as well affect the choices nosotros make. To sympathise how anchoring works, imagine you're shopping for a used automobile at a local dealership. The model you similar is priced at $9,999.
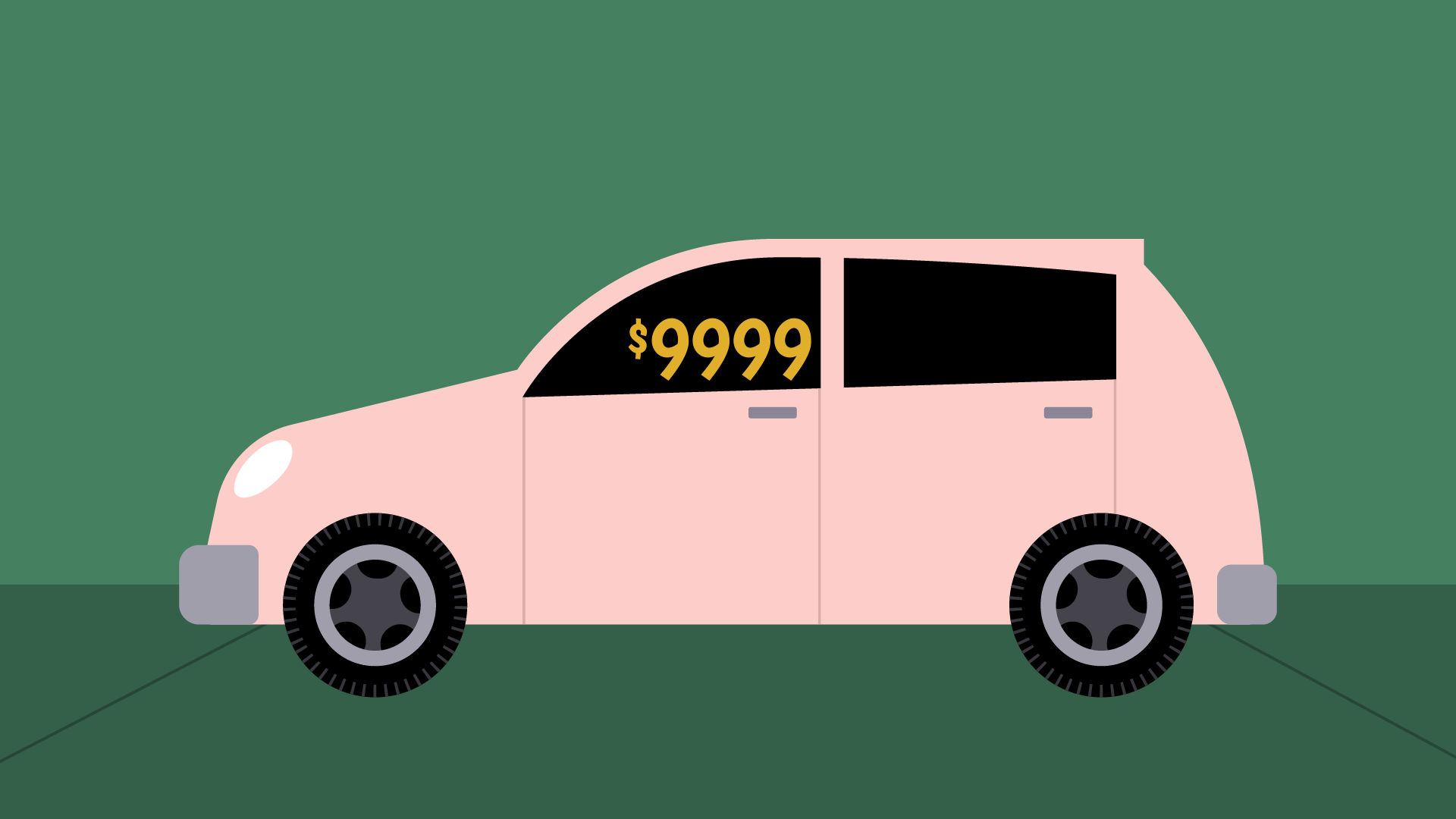

Next, imagine the dealer offers you a disbelieve. The automobile is now $8,999, a full thou dollars less. Sounds like a can't-miss opportunity, right? Non necessarily.

Anchoring suggests that nosotros rely besides heavily on the first matter nosotros hear (in this case, the initial cost of the car). That'south what makes the discount then appealing, but it shouldn't be the deciding gene. There are also more objective things to consider, like how much the car is really worth, and whether you can observe a meliorate price elsewhere. If y'all're not careful, the anchoring issue tin can weigh you lot downwards.

Option overload
Cognitive biases aren't the merely things that can bear upon decision-making. More and more studies show that stress tin can have an impact—both on the quality of our decisions and on our ability to make them. Take this well-known study near jam.
At an upscale food market, researchers set upward two displays offering free samples of jam. 1 gave customers half dozen different flavors to choose from; the other gave them 24.
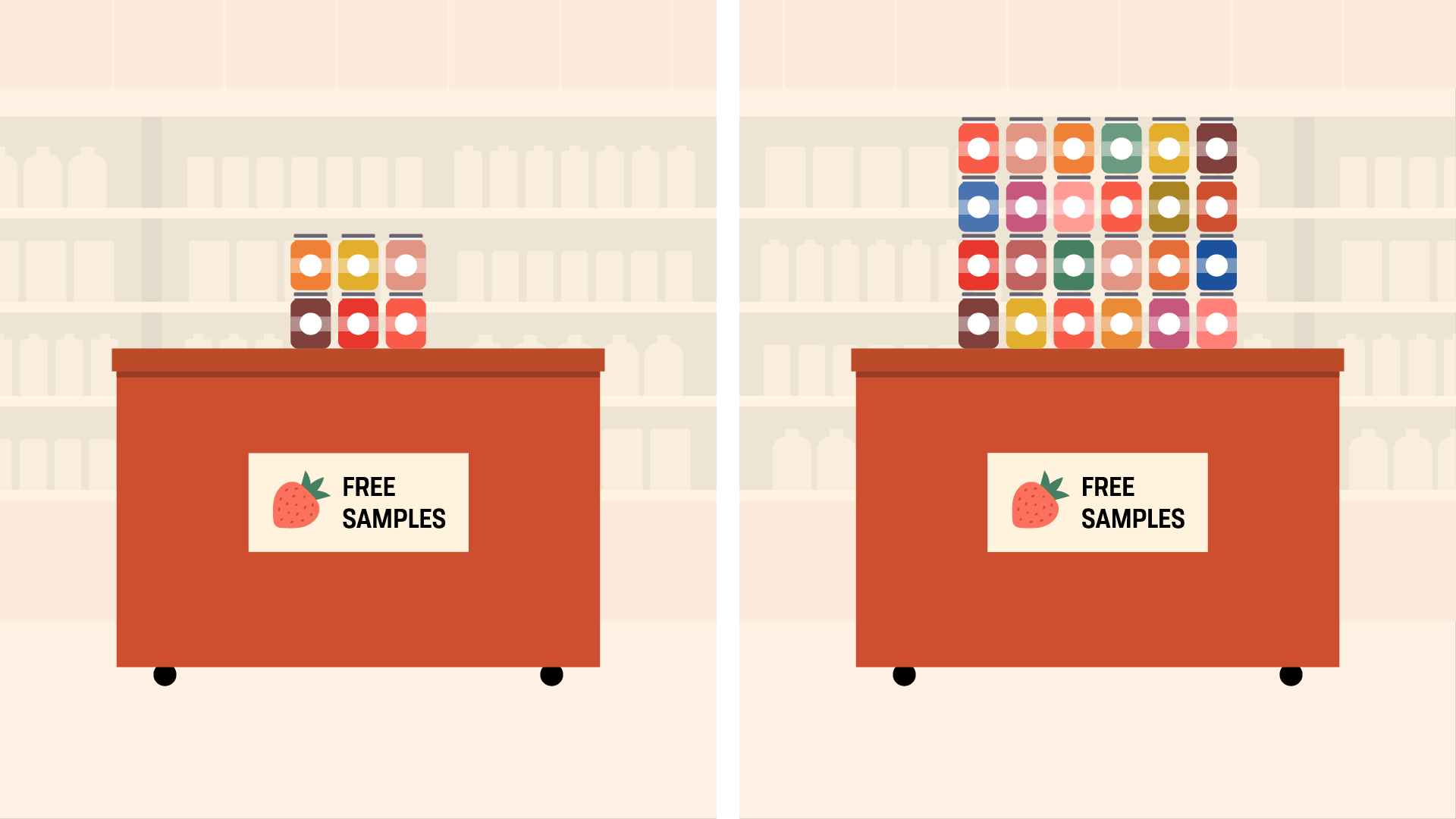

The larger display attracted more people, only they were vi times less likely to really buy a jar of jam (compared to those who visited the smaller brandish). The reason for this is a phenomenon now known every bit choice overload.
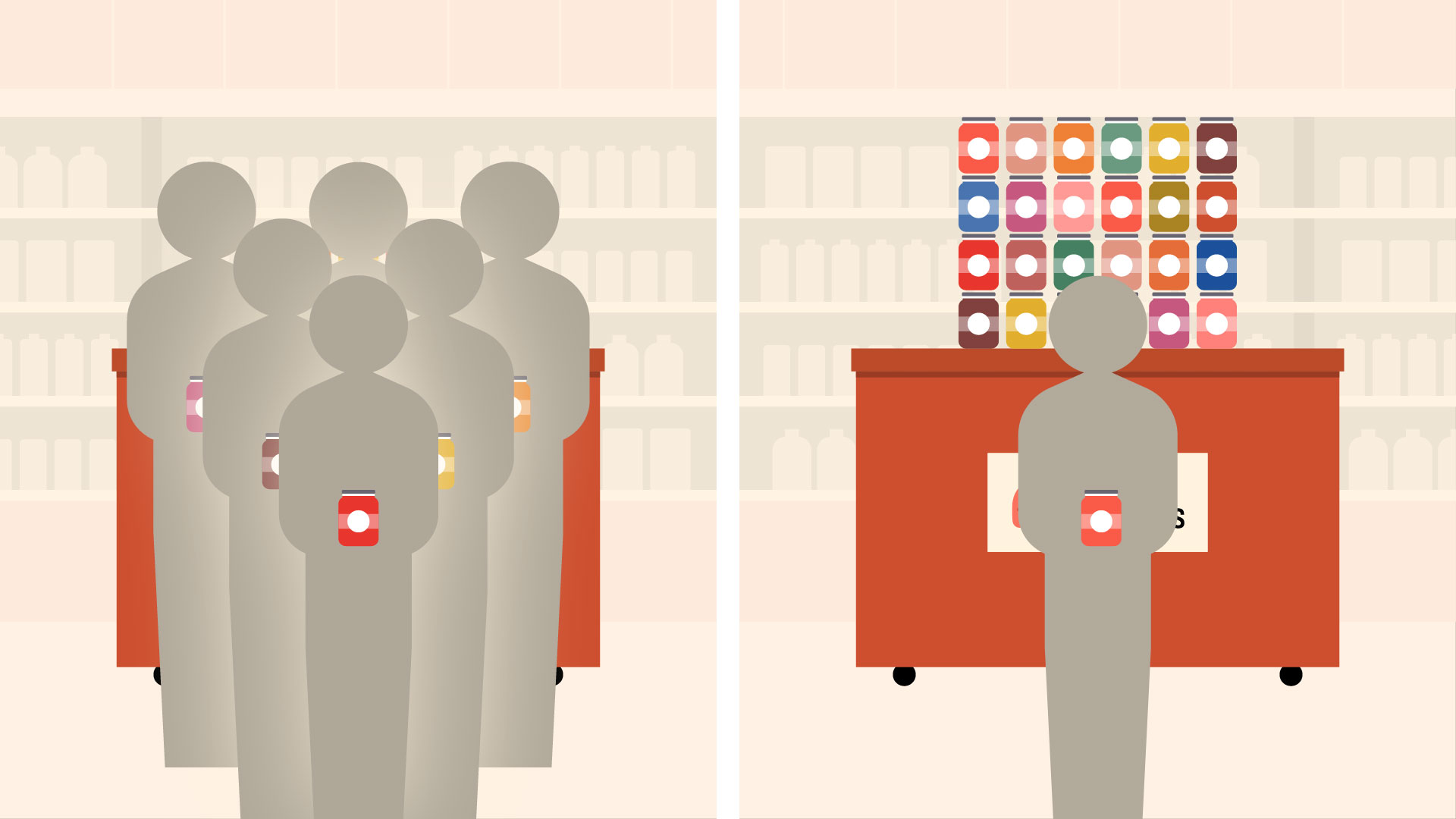
Choice overload tin can happen any time we feel overwhelmed by the sheer number of options. We have such a hard time comparing them that nosotros're less likely to choose anything at all. As in the jam example, many of us would sooner walk away empty-handed than deal with the stress of choosing from such a big selection.

Decision fatigue
A similar thing happens when we're forced to brand multiple decisions one after another—a common occurrence in everyday life. Nosotros experience an outcome psychologists phone call decision fatigue.
Decision fatigue suggests that making a large number of decisions over a prolonged period of time can be a significant drain on our willpower. The effect? Nosotros have a harder time maxim no—to things like junk food, impulse buys, and other tempting offers.

On the flip side, fatigue can also get in harder to say yes, especially to decisions that would upset the status quo.

Fatigue makes it difficult to even think most making decisions, let alone what's correct or incorrect, correct or incorrect. We follow the path of least resistance because it's the easiest affair to practise.
The upside of dubiety
Making decisions will ever be difficult because information technology takes time and energy to weigh your options. Things similar second-guessing yourself and feeling indecisive are just a part of the procedure.

In many ways, they're a good thing—a sign that y'all're thinking about your choices instead of just going with the catamenia. That'south the get-go step to making amend, more thoughtful decisions.
/en/trouble-solving-and-controlling/decisionmaking-strategies/content/
Source: https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/problem-solving-and-decision-making/why-is-it-so-hard-to-make-decisions/1/
0 Response to "Why Is It Harder to Read With Contacts"
Post a Comment